Evaluation of a furochromone from the halophyte Corydalis heterocarpa for cytotoxic activity against human gastric cancer (AGS) cells
Abstract
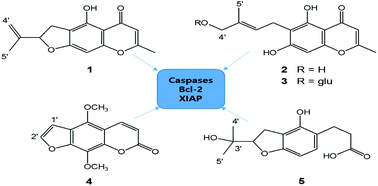
A furochromone, heterocarpin (1), was isolated from the halophyte Corydalis heterocarpa, along with four known compounds (2–5), which were obtained for the first time from this genus. The chemical structures of these compounds were determined by extensive 2-D NMR experiments and by comparison with the data reported in the literature. Compound 1 showed significant cytotoxic activities against four human cancer cells, AGS (human gastric cancer), HT-29 (human colon cancer), HT-1080 (human fibrosarcoma) and MCF-7 (human breast carcinoma). According to the cytotoxicity results, the mechanism behind the cytotoxic presence of compound 1 on AGS cells was investigated through the mRNA and protein levels of apoptotic pathway factors such as p21, p53, Bax, Bcl-2, XIAP, and caspases-3 and -9. The results indicated that heterocarpin (1) showed the cytotoxic effect on cancer cells by inducing apoptosis via regulated Bax-Bcl-2 ratio, overproduced caspases and suppressed XIAP. The inhibition of NFκB and activation of JNK and ERK pathways were also observed in the presence of heterocarpin (1). Therefore, heterocarpin and its source C. heterocarpa were suggested to be utilized as a functional food with potential pro-apoptotic activity against cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...