Microencapsulated cells of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei in biopolymer complex coacervates and their function in a yogurt matrix
Abstract
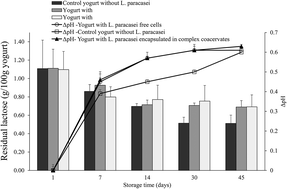
L. paracasei subsp. paracasei E6 cells were encapsulated by complex coacervation using whey protein isolate (WPI) and gum arabic and introduced in stirred yogurts after fermentation. For comparison purposes, yogurts without addition of L. paracasei and yogurts with free cells of L. paracasei were produced. The survival of free and microencapsulated L. paracasei cells was evaluated during storage of the yogurts for 45 days at 4 °C. In addition, yogurts were exposed to simulated gastric juice and the reduction in viable numbers of L. paracasei cells was assessed. The effect of complex coacervates’ addition on the rheological properties of yogurts was also evaluated. Yogurts containing encapsulated L. paracasei cells showed a slightly improved cell survival (≤0.22 log CFU g−1 reduction) during storage when compared to yogurts containing free cells (≤0.64 log CFU g−1 reduction). Moreover, the microencapsulated L. paracasei cells exhibited greater survival compared to free cells upon exposure of the yogurt samples to simulated gastric juice (pH 2.0) for 3 h. Finally, the incorporation of complex coacervates did not significantly affect the rheological properties of yogurts especially when added at concentrations less than 10% w/w. Consequently, the inclusion of microencapsulated bacteria by complex coacervation in yogurts, could become an effective vehicle for successful delivery of probiotics to the gut, and hence contributing to the improvement of the gastrointestinal tract health, without altering the texture of the product.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Structure & Sensory

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...