Phenolic recovery and bioaccessibility from milled and finished whole grain oat products†
Abstract
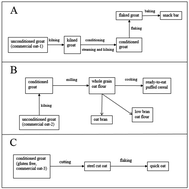
While much is known about the benefits of oat fiber, the relevance of phenolics from oat based food products remains unclear. To gain insight into the relevance of phenolics from consumer oat products, the content of phenolics and avenanthramides (AVEs) was followed in 10 oat cultivars as well as milled oat ingredients and ready to eat (RTE) consumer products (puffed cereals and snack bars). Free phenolic content ranged from 17.2 to 228.1 μg g−1 DW with AVEs accounting for 57.3–90.6% of the total free phenolics. Bound phenolic content ranged from 141.4 to 680.9 μg g−1 DW with ferulic acid accounting for 62–94% of the bound phenolics. Select oat groats were ground to flour and prepared as wet cooked porridges (∼20% oat flour in boiling water) or introduced as RTE products into a three stage in vitro digestion to determine phenolic bioaccessibility. The relative bioaccessibility for wet cooked porridges ranged from 0.3–2.6% and from 2.9–28.8% for individual phenolic acids and AVEs, respectively. Puffed oat cereal had significantly higher bioaccessibility compared to matching wet-cook porridge made from the same oat flour (e.g. 83.8% versus 19.1% for AVE A; p < 0.05). Intestinal uptake of bioaccessible oat phenolics from digesta was confirmed by experiments with Caco-2 human intestinal cells. The overall intestinal uptake of oat phenolics was low, ranging between 0.16% and 2.71% across digesta from all oat products. In conclusion, these experiments demonstrate that phenolics naturally present in whole grain oats are recovered well through traditional grain processing, milling and food processing. Furthermore, processing of oat cultivars into a RTE cereal may have a positive impact on the digestive release and bioaccessibility of oat phenolics in the upper GI tract.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...