Enhanced adsorption and degradation of phenolic pollutants in water by carbon nanotube modified laccase-carrying electrospun fibrous membranes†
Abstract
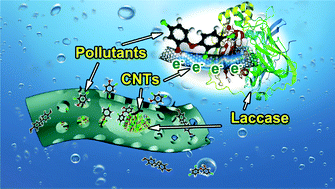
Multi-walled carbon nanotube modified laccase-carrying electrospun fibrous membranes (MWCNTs-LCEFMs) were fabricated via co-electrospinning a poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA)/laccase/MWCNT mixed solution. A triblock copolymer PEO–PPO–PEO (F108) was added as an emulsifier to promote the dispersion of the laccase and acid-treated short MWCNTs in the electrospinning solution. The characterization results illustrated that the electrospun nanofibers possess a feature of being bead-free, porous and having a core–shell structure, with active laccase encapsulated inside the fibers and one end of some MWCNTs inserted into the edge of the pores. After being modified by a small amount (1.5 wt%, vs. PDLLA) of MWCNTs, the specific surface area and mechanical tensile strength of MWCNTs-LCEFMs were enhanced by about 2 and 3 times compared to those of LCEFMs, respectively. The MWCNTs-LCEFMs were applied to remove the widespread phenolic organics from water, including bisphenol A (BPA), triclosan (TCS) and 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). Benefiting from the improved adsorption property for substrates and the promoted electron transfer in the laccase-catalytic reaction, the MWCNTs-LCEFMs showed higher activity recovery (88.9% vs. free laccase), and better storage and operational stability than LCEFMs. In addition, the adsorption efficiencies of MWCNTs-LCEFMs for BPA and 2,4-DCP were enhanced by more than 50%. The removal efficiencies of MWCNTs-LCEFMs for 2,4-DCP, BPA and TCS reached 92.6 ± 0.74%, 95.5 ± 0.46% and 99.7 ± 0.02%, respectively, with the degradation efficiencies reaching 81.7 ± 1.9%, 90.5 ± 1.1% and 85.6 ± 1.5%, respectively. Meanwhile, the removal half-life (t1/2) of 2,4-DCP, BPA and TCS by the MWCNTs-LCEFMs was shortened to 7.9 ± 0.07, 4.7 ± 0.04 and 0.76 ± 0.01 min, respectively. The removal mechanism of these phenolic pollutants by MWCNTs-LCEFMs was considered as a synergistic effect of membrane adsorption and laccase degradation, where the catalytic degradation of laccase was obviously strengthened by the improved adsorption (pre-concentration) process of the fibers and MWCNTs, and the enhanced electron transfer process of MWCNTs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...