Fluorescently labelled SiO2 nanoparticles as tracers in natural waters: dependence of detection limits on environmental conditions†
Abstract
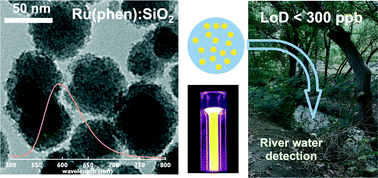
The identification of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) in the environment is of uttermost importance, in view of the possibility of harmful effects on living organisms. While it is clear that monitoring their presence and accumulation is essential in any risk assessment scenario, this is a challenging task. On the one hand, ENMs are present at trace concentration levels, requiring extremely sensitive sampling and analysis methods. On the other hand, specific identification of ENMs is further complicated by the simultaneous presence of other nanomaterials (often analogous in terms of size and properties) already present in the environment. Therefore, the development of labels that allow unequivocal, highly sensitive identification of specific nanomaterials is desirable. Here, we report the development of stable fluorescent labels for silica (SiO2) nanoparticles. The markers developed allow monitoring of their presence in environmentally relevant media at low detection levels. Identification of labelling signals has been performed using both online and offline techniques under a variety of conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...