Developing the family of picolinate ligands for Mn2+ complexation†
Abstract
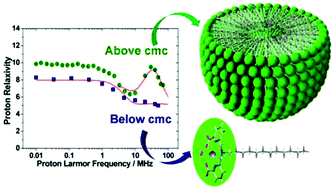
We have reported here a series of ligands containing pentadentate 6,6′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dipicolinic acid units that differ in the substituent present at the amine nitrogen atom (acetate: H3DPAAA; phenyl: H2DPAPhA; dodecyl: H2DPAC12A; 4-hexylphenyl: H2DPAC6PhA). The protonation constants of the hexadentate DPAAA3− and pentadentate DPAPhA2− ligands and the stability constants of their Mn2+ complexes were determined using pH-potentiometry (25 °C, 0.15 M NaCl). The mono-hydrated [Mn(DPAAA)]− complex (log KMnL = 13.19(5)) was found to be considerably more stable than the bis-hydrated [Mn(DPAPhA)] analogue (log KMnL = 9.55(1)). A detailed 1H and 17O NMR relaxometric study was carried out to determine the parameters that govern the proton relaxivities of these complexes. The [Mn(DPAC12A)] complex, which contains a dodecyl lipophilic chain, forms micelles in solution characterized by a critical micellar concentration (cmc) of 96(9) μM. The lipophilic [Mn(DPAC6PhA)] and [Mn(DPAC12A)] derivatives form rather strong adducts with Human Serum Albumin (HSA) with association constants of 7.1 ± 0.1 × 103 and 1.3 ± 0.4 × 105 M−1, respectively. The X-ray structure of the complex {K(H2O)4}{[Mn(DPAAA)(H2O)]}2 shows that the Mn2+ ion in [Mn(DPAAA)]− is coordinated to the six donor atoms of the ligand, a coordinated water molecule completing the pentagonal bipyramidal coordination environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...