A gadolinium(iii) complex based dual-modal probe for MRI and fluorescence sensing of fluoride ions in aqueous medium and in vivo†
Abstract
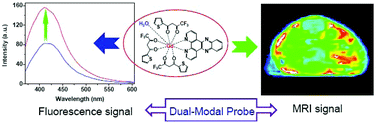
A novel Gd(III) complex, Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ, was designed and assembled as a dual-modal probe for the simultaneous fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detection of fluoride ions in aqueous media and in vivo. In this system, the Gd(III) center is not only serving as a MRI signal output unit, but also as a binding site for fluoride ions. When appropriate equivalents of fluoride ions were added into the solution of Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ, the replacement of the coordination water led to a decrease of the longitudinal relaxivity (r1) as well as distinct spectroscopic changes, by which MRI/fluorescence dual-modal fluoride ion sensing was achieved. In the presence of fluoride ions, a 2-fold fluorescence emission enhancement of Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ, and a notable decrease of the UV–vis absorption spectrum were observed. The fluorescence detection limit for fluoride ions was established at 70 nM. Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ also exhibits about 75% decrease of the longitudinal relaxivity (r1) upon addition of fluoride ions in aqueous medium. The appropriate blood circulation time of Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ allows its potential application in MRI in vivo. The results demonstrated that Gd(TTA)3-DPPZ could serve as a potential MRI/fluorescence bimodal imaging agent for the specific and high-sensitive sensing of fluoride ions in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...