Visible/near-IR-light-driven TNFePc/BiOCl organic–inorganic heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity
Abstract
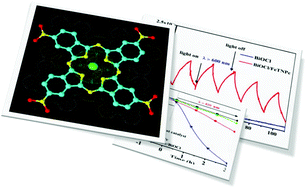
Although semiconductor photocatalysis has been reported for more than 40 years, the spectral response is still focused on the region of UV-Visible and it is seldom extended to more than 600 nm. In this work, visible/near-IR-light-driven 2,9,16,23-tetranitrophthalocyanine iron (FeTNPc)/bismuth oxychloride (BiOCl) organic–inorganic heterostructures have been synthesized by a two-step solvothermal method. The obtained products were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectra, scanning electron and transmission microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer, UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, nitrogen adsorption–desorption, and electrochemical measurements. The photocatalytic activity for the decomposition of methyl orange and bisphenol A solution can be significantly improved under visible/near-IR-light irradiation. Through detecting the main oxidative species by trapping experiments, the results show holes and ˙O2− radicals are majorly and minorly responsible for photodegradation respectively. What's more, the FeTNPc/BiOCl composite photocatalyst still retained the photocatalytic activity after three cycle measurements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...