Aluminum chelates supported by β-quinolyl enolate ligands: synthesis and ROP of ε-CL†
Abstract
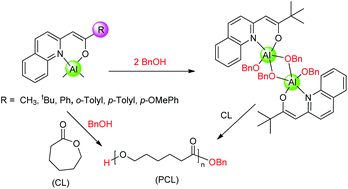
Treatment of tautomers of β-quinolyl ketone-enaminones 1a–6a with AlMe3 afforded β-quinolyl enolato dialkylaluminium complexes LAlMe21b–6b (L = [(2-C9H6N)–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(R)–O–], R = CH3 (1b), tBu (2b), Ph (3b), o-tolyl (4b), p-tolyl (5b), p-OMePh (6b)), respectively. 2b reacted with benzyl alcohol to generate the corresponding LAl(OBn)2 complex 2c. Complexes 1b–6b and 2c were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, elemental analyses and single crystal X-ray diffraction analyses. All complexes were tested as catalyst precursors for ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone (ε-CL). The results indicated that LAlMe2 (1b–6b) exhibited good activity towards the ROP of ε-CL in the presence of benzyl alcohol at 80 °C, and LAl(OBn)22c exhibited higher catalytic activity in the absence of alcohol than 1b–6b for the ROP of ε-CL. However, both polymerizations were less controlled. Kinetic studies showed that the polymerization reaction catalyzed by 1b–6b and 2c proceeded with first-order dependence on the monomer and took place through coordination–insertion.
C(R)–O–], R = CH3 (1b), tBu (2b), Ph (3b), o-tolyl (4b), p-tolyl (5b), p-OMePh (6b)), respectively. 2b reacted with benzyl alcohol to generate the corresponding LAl(OBn)2 complex 2c. Complexes 1b–6b and 2c were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, elemental analyses and single crystal X-ray diffraction analyses. All complexes were tested as catalyst precursors for ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone (ε-CL). The results indicated that LAlMe2 (1b–6b) exhibited good activity towards the ROP of ε-CL in the presence of benzyl alcohol at 80 °C, and LAl(OBn)22c exhibited higher catalytic activity in the absence of alcohol than 1b–6b for the ROP of ε-CL. However, both polymerizations were less controlled. Kinetic studies showed that the polymerization reaction catalyzed by 1b–6b and 2c proceeded with first-order dependence on the monomer and took place through coordination–insertion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...