Hydrogen atom transfer reactions of ferrate(vi) with phenols and hydroquinone. Correlation of rate constants with bond strengths and application of the Marcus cross relation†
Abstract
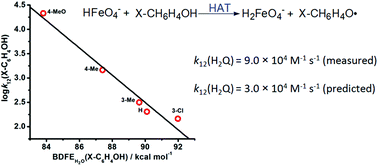
The oxidation of phenols by HFeO4− proceeds via a hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) mechanism, as evidenced by a large deuterium isotope effect and a linear correlation between the log(rate constant) and bond dissociation free energy (BDFE) of phenols. The Marcus cross relation has been applied to predict the rate constant of HAT from hydroquinone to HFeO4−.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...