Superior performance of CuInS2 for photocatalytic water treatment: full conversion of highly stable nitrate ions into harmless N2 under visible light†
Abstract
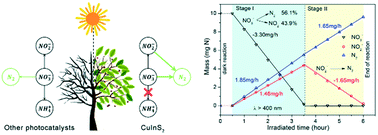
Photocatalytic nitrate removal is potentially a green and low-cost technique for water purification; however, no effective visible light photocatalyst has been developed during the past thirty years. Here, we prove that CuInS2 (CIS) is a highly efficient visible light photocatalyst for nitrate removal. By the simultaneous loading of Pt, Ru and Au, it exhibited a high record of nitrate conversion rate of 8.32 mg N h−1 under pure visible light (λ > 400 nm). Highly concentrated NO3− (100 ppm N) can be completely converted into N2 in a few hours, without any over-reduction to ammonia nor production of H2. Under the irradiation of a monochromatic beam from 400 to 650 nm, CIS was most sensitive at 500 nm with an optimal apparent quantum yield of 23.85%. The mechanism was proposed as adsorption–reduction reactions and supported by the fact that the photocatalytic efficiency decreased when halogen ions were added as competing anions. The necessity of using a sacrificial agent during nitrate reduction was validated by a thorough discussion. Herein CIS remained effective when various or harmless sacrificial agents were used. Our work presents a new generation of photocatalysts for nitrate removal and pushes it forward to possible applications in industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...