Co-decorated Cu alloy catalyst for C2 oxygenate and ethanol formation from syngas on Cu-based catalyst: insight into the role of Co and Cu as well as the improved selectivity†
Abstract
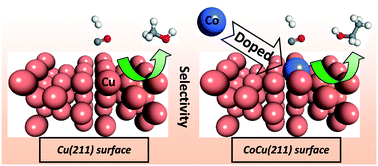
Co-decorated Cu alloy, a potential material for use in syngas conversion based on less expensive Cu metal, can efficiently promote the formation of C2 oxygenates and ethanol. Herein, the mechanisms of C2 oxygenate and ethanol formation from syngas on Co-decorated Cu alloy catalyst have been investigated to probe into the role of Co and Cu and identify the catalytic selectivity of Cu catalysts toward C2 oxygenates and ethanol. DFT calculations with microkinetic modeling have been performed, and the Co-decorated Cu alloy catalyst is modeled using Co-doped Cu(211) surface. Our results suggest that CO initial adsorption and activation occur at the Cu sites of Co-doped Cu(211). CO prefers to be hydrogenated to CHO at the Cu site, and subsequently, CHO species at the Cu site easily migrate to the most stable Co–Cu mixed site. Starting from CHO species adsorbed at the Co–Cu mixed site, CH2 and CH3 species are the most favorable CHx monomers formed via H-assisted CHxO (x = 2, 3) dissociation, which are more favorable than CH3OH formation both thermodynamically and dynamically, suggesting that the CoCu(211) surface can provide more CHx resources for C–C chain formation. Further, starting from CH2 and CH3 species, ethanol is formed by CO insertion into CH2 and CH3 to CH2CO and CH3CO, respectively; subsequently, CH2CO and CH3CO are successively hydrogenated to ethanol via CH2CHO, CH3CHO and CH3CH2O intermediates. Based on microkinetic modeling, the CoCu(211) surface is highly selective for ethanol rather than methanol and methane. Moreover, the function of Cu is to provide the undissociated CO/CHO at the Cu sites; Co promotes CHx formation by accelerating the C–O bond cleavage of CHxO species, and the synergetic effect of Co and Cu facilitates C–C chain formation, which is typical of a “dual-site” mechanism. Thus, the synergetic effects between the active Co and Cu sites promote the formation of C2 oxygenates and ethanol; the productivity and selectivity of ethanol over the Co-decorated Cu-based catalyst can be improved compared to that of the pure Cu catalyst. In addition, we believe that the insight derived from this study can be valuable for the design of other types of Cu-based catalysts involved in C2 oxygenate synthesis from syngas.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...