Visible light driven hydrogen evolution with a noble metal free CuGa2In3S8 nanoparticle system in water†
Abstract
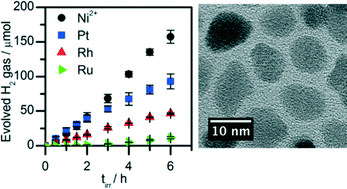
CuGa2In3S8 (CGIS) nanoparticles were synthesised by a hot-injection method and rendered water dispersible by modification with the hydrophilic ligand 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA). The CGIS nanoparticles were characterised by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron, diffuse reflectance and infrared spectroscopy as well as inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. Photocatalytic H2 production using the MPA modified CGIS nanoparticles and a nickel salt under visible light irradiation was achieved from acidic solution (pH 2.6) with ascorbic acid as a sacrificial electron donor. Previously, CGIS required the presence of a precious metal co-catalyst and sulfide ions as a sacrificial reagent in alkaline solution to display photocatalytic activity for H2 generation. In the reported system, visible light irradiation of the MPA modified CGIS nanoparticles with a Ni salt displayed even superior sacrificial H2 evolution activity than when employing the precious metals Pt, Rh and Ru. An external quantum efficiency of more than 12% was achieved at λ = 540 nm, which is almost twice that previously reported for CGIS nanoparticles in the presence of a noble metal co-catalyst and sulfide ions as an electron donor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...