Insight into reaction pathways in CO hydrogenation reactions over K/MoS2 supported catalysts via alcohol/olefin co-feed experiments†
Abstract
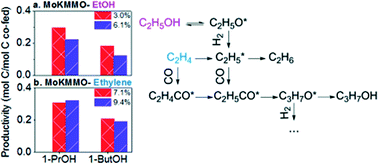
Reaction pathways for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas are studied over K/MoS2 domains supported on mesoporous carbon (C) and mixed MgAl oxide (MMO) via addition of methanol, ethanol, and ethylene co-feeds. A methanol co-feed results in an increase in ethanol and methane production for the catalysts studied. Ethanol or ethylene co-feeds yield increased C3+OH and C2+HC over the supported catalysts. No change is observed in the product distribution over K/bulk-MoS2 with an ethanol co-feed, but 1-propanol production significantly increases in the presence of ethylene, suggesting the formation of ethyl species from ethanol and/or the adsorption of ethanol are rate-controlling for 1-propanol formation when ethanol is co-fed. Ethylene and ethanol co-feeds yield similar production rates of C3+OH over the MMO catalyst, indicating that alcohol formation likely proceeds primarily via the same acyl intermediate as olefin carbonylation. Supports do seem to have an important influence on the reaction pathways. Specifically, acidic carbon support seems to facilitate alcohol dehydration/hydrogenation to produce alkanes, while MMO influences methanol plus 1-propanol coupling to form isobutyl alcohol. However, Mo–K–MMO sites are key for superior normalized C3+OH productivity with ethanol and ethylene co-feeds over the MMO catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...