Effects of carbon surface topography on the electrode/electrolyte interface structure and relevance to Li–air batteries
Abstract
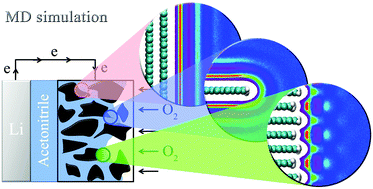
This work is focused on the effect of the electrode/electrolyte interface restructuring under the variation of carbon surface topography, as one of the possible factors determining the electrochemical activity of different carbon materials in Li–air batteries. Molecular dynamics simulation was used to investigate an acetonitrile-based electrolyte in contact with the following carbon surfaces: graphene plane, single-layer graphene edge, and multi-layer graphene edge. It was shown that the surface topography strongly influences the electrolyte structure at the interface. Acetonitrile has a layered structure at the plane and the edge of graphene nanoribbons and a qualitatively different chessboard structure at the multi-layer graphene edge. It was found from the potentials of mean force that the variation of the surface topography induces the redistribution of the reactants Li+ and O2 near the surface and influences their adsorption rate. This should affect the kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction and may explain massive deposition of discharge products on graphene edges in Li–air batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...