Evidence for dissolved hydrogen in the mixed ionic–electronic conducting perovskites La0.6Sr0.4FeO3−δ and SrTi0.7Fe0.3O3−δ
Abstract
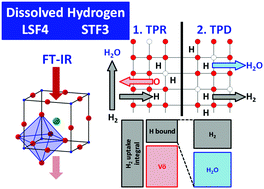
Two mixed ionic–electronic conducting, Fe-containing perovskites were investigated regarding their reducibility in dry H2, namely lanthanum strontium ferrite (LSF4, La0.6Sr0.4FeO3−δ) and strontium titanium ferrite (STF3, SrTi0.7Fe0.3O3−δ). Upon treatment under comparable reduction conditions, LSF4 is by far more affected by reduction and is reduced more deeply than STF3. Thermal treatments of fully oxidized or slightly reduced LSF4/STF3 at decreased O2 partial pressure lead to spontaneous desorption of O2. Temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) spectra of H2 reveal distinct differences in H2 and H2O desorption. A simple mass balance of H2 reveals that oxygen vacancies formed on STF3 are more resilient towards O2 re-oxidation compared to those on LSF4. The results also imply that substantial amounts of hydrogen are dissolved in the bulk of LSF4 or STF3. 4.9 × 10−2 mol H2 per mol LSF4 and 1.6 × 10−2 mol H2 per mol STF3 are incorporated if the specimens are heated in flowing/dry H2 up to 550 °C and 612 °C, respectively. For LSF4 this equals about 13 hypothetical ML of H2 and for STF3 about 20 hypothetical ML of H2. This conclusion is also supported by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). FT-IR reveals water formation during static H2 treatment of LSF4/STF3, which indicates perovskite reduction. Furthermore, both samples behave extraordinarily hydrophobic and no chemistry involving surface hydroxy groups was observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...