pH controlled adsorption of water-soluble ruthenium clusters onto carbon nanotubes and nanofiber surfaces†
Abstract
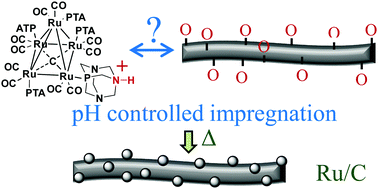
Supported catalysts were prepared from water-soluble molecular clusters by pH controlled impregnations in order to probe the interactions occurring between the supports and the clusters and to maximize them. The PZC of different nano-carbon solids (nanotubes and nanofibers) was determined. The EpHL method of measuring the PZC could be successfully extended for the first time to these nano-carbon supports. When impregnating these nano-carbons with water-soluble Ru clusters by varying the pH, we found that two adsorption mechanisms were taking place. We postulate that interactions in the form of π-bond coordination or reactions with higher reactivity zones of the carbon surface occur at all pH values. Electrostatic interactions coexist with the latter and play a determining role, allowing or hindering maximal adsorption. Our water-impregnated samples exhibit smaller and better distributed nanoparticles in comparison to an organic-solvent-impregnated sample. Sintering of the particles at higher activation temperature led to nanoparticles with a bimodal size distribution on the nanofibers. The bimodal size distribution is a strong indication of two different adsorption mechanisms. The obtained Ru/nano-C catalysts present a valuable activity and selectivity in the hydrogenation of lactose into lactitol.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...