A comparative study of Ni–Mn layered double hydroxide/carbon composites with different morphologies for supercapacitors
Abstract
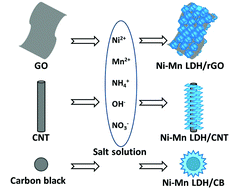
A variety of carbon materials varying from 0D to 2D, i.e. 0D nanoparticles, 1D carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and 2D reduced graphene oxide (rGO) are selected to in situ combine with Ni–Mn layered double hydroxide (LDH) to prepare electrode materials for supercapacitors. Through a simple solution method, hierarchical Ni–Mn LDH/carbon composites can be easily fabricated. A comparative study is carried out on the sandwich-like LDH/rGO, flower-like LDH/carbon black, turbostratic-structured LDH/CNTs and ternary LDH/CNTs/rGO for their structure, morphology, porous properties and electrochemical performances. The results show that the ternary Ni–Mn LDH/CNTs/rGO composite yields the highest specific capacitance of 1268 F g−1 in 2 M KOH electrolyte and a long lifespan, exhibiting great potential for supercapacitor applications. Meanwhile, investigation on the influence of the cation species of MOH (M = Li+, Na+ or K+) and the alkali concentration of the KOH electrolyte illustrates that increasing the concentration of the KOH electrolyte can benefit the capacitive performance of the electrode and that NaOH shows great advantages as an electrolyte for the Ni–Mn LDH/CNTs/rGO electrode due to its high capacitance and small resistance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...