Secondary brown carbon formation via the dicarbonyl imine pathway: nitrogen heterocycle formation and synergistic effects†
Abstract
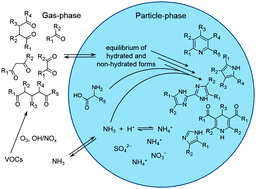
Dicarbonyls are known to be important precursors of so-called atmospheric brown carbon, significantly affecting aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing. In this systematic study we report the formation of light-absorbing nitrogen containing compounds from simple 1,2-, 1,3-, 1,4-, and 1,5-dicarbonyl + amine reactions. A combination of spectrophotometric and mass spectrometric techniques was used to characterize reaction products in solutions mimicking atmospheric particulates. Experiments with individual dicarbonyls and dicarbonyl mixtures in ammonium sulfate and glycine solutions demonstrate that nitrogen heterocycles are common structural motifs of brown carbon chromophores formed in such reaction systems. 1,4- and 1,5-dicarbonyl reaction systems, which were used as surrogates for terpene ozonolysis products, showed rapid formation of light-absorbing material and products with absorbance maxima at ∼450 nm. Synergistic effects on absorbance properties were observed in mixed (di-)carbonyl experiments, as indicated by the formation of a strong absorber in ammonium sulfate solutions containing acetaldehyde and acetylacetone. This cross-reaction oligomer shows an absorbance maximum at 385 nm, relevant for the actinic flux region of the atmosphere. This study demonstrates the complexity of secondary brown carbon formation via the imine pathway and highlights that cross-reactions with synergistic effects have to be considered an important pathway for atmospheric BrC formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...