Protonation induces base rotation of purine nucleotides pdGuo and pGuo†
Abstract
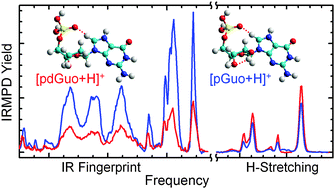
Infrared multiple photon dissociation (IRMPD) action spectra of the protonated forms of 2′-deoxyguanosine-5′-monophosphate and guanosine-5′-monophosphate, [pdGuo+H]+ and [pGuo+H]+, are measured over the IR fingerprint and hydrogen-stretching regions using the FELIX free electron laser and an OPO/OPA laser system. Electronic structure calculations are performed to generate low-energy conformations of [pdGuo+H]+ and [pGuo+H]+ and determine their relative stabilities at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2d,2p)//B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) and MP2(full)/6-311+G(2d,2p)//B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) levels of theory. Comparative analyses of the measured IRMPD action spectra and B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) linear IR spectra computed for the low-energy conformers are performed to determine the most favorable site of protonation and the conformers present in the experiments. These comparisons and the computed energetics find that N7 protonation is considerably preferred over O6 and N3, and the N7 protonated ground-state conformers of [pdGuo+H]+ and [pGuo+H]+ are populated in the experiments. The 2′-hydroxyl substituent does not significantly impact the stable low-energy conformers of [pdGuo+H]+vs. those of [pGuo+H]+. The effect of the 2′-hydroxyl substituent is primarily reflected in the relative intensities of the measured IRMPD bands, as the IRMPD profiles of [pdGuo+H]+ and [pGuo+H]+ are quite similar. Comparisons to previous IRMPD spectroscopy investigations of the protonated forms of the guanine nucleosides, [dGuo+H]+ and [Guo+H]+, and deprotonated forms of the guanine nucleotides, [pdGuo–H]− and [pGuo–H]−, provide insight into the effects of the phosphate moiety and protonation on the conformational features of the nucleobase and sugar moieties. Protonation is found to induce base rotation of the guanine residue to an anti orientation vs. the syn orientation found for the deprotonated forms of the guanine nucleotides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...