Crystal growth and physical properties of the organic salt benzimidazolium 3-nitrophthalate†
Abstract
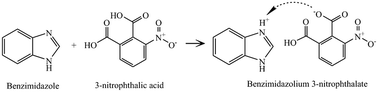
From the point of view of crystal growth and design, it is interesting to study the effect of different isomers on the resulting structure. Single crystals of the organic salt benzimidazolium 3-nitrophthalate (BZD+·mNPA−) have been grown by slow evaporation from methanol solution. Single crystal X-ray diffraction demonstrated that the crystal structure belongs to the monoclinic system with space group P21/c. The properties of the functional groups have been studied by FTIR spectroscopy, FT-Raman spectral analysis and 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The emission spectra of BZD+·mNPA− were recorded in different solvents; they exhibit a negative solvatochromatic effect when the polarity of the solvent is increased. The thermal stability, dielectric constant and dielectric loss have been investigated and the HOMO and LUMO energy levels have been calculated using density functional theory (DFT). The crystal structure of BZD+·mNPA− has been compared with that of benzimidazolium 2-nitroterephthalate (BZD+·NTPh−). The interactions of the isomers 3-nitrophthalate or 2-nitroterephthalate salts with benzimidazolium are very similar; however, the different positions of the carboxyl groups on the benzene rings changes the layout of the structure, which leads to undulating sheets for 3-nitrophthalate and flat antiparallel sheets for 2-nitrotherephthalate. The salt decomposes at around 180 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...