Employing mixed-ligand strategy to construct a series of luminescent Cd(ii) compounds with structural diversities†
Abstract
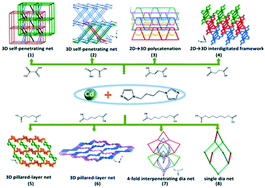
Eight new cadmium compounds, namely, {Cd2(ox)2(bib)1.5}n (1), {Cd(mal)(bib)0.5}n (2), {Cd(fum)(bib)(H2O)}n (3), {Cd2(suc)(bib)(NO3)2(H2O)}n (4), {Cd2(glu)2(bib)}n (5), {Cd(adp)(bib)}n (6), {[Cd(sub)(bib)]·(H2O)3}n (7) and {[Cd(aze)(bib)1.5]·(H2O)5}n (8) (bib=1,4-bis(N-imidazolyl)butane, H2ox = oxalic acid, H2mal = malonic acid, H2fum = fumaric acid, H2suc = succinic acid, H2glu = glutaric acid, H2adp = adipic acid, H2sub = suberic acid, and H2aze = azelaic acid) were constructed from flexible bis(imidazole) ligands incorporating a variety of aliphatic dicarboxylic acids. They were characterized using elemental analysis, IR, powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 exhibits a 3D self-penetrating framework with a novel {44·54·62·74·8}{53·62·7}2 topology that can interestingly be regarded as a cross-link of two interpenetrating pcu networks. Compound 2 displays a six-connected self-penetrating pillared-layer framework with a roa topology. The structure of 3 is an unprecedented 2D → 3D polycatenation based on a (42·64) bilayer. If hydrogen bonding interactions are taken into account, the resulting structure displays a 3-fold interpenetrated 3D rob network. Compound 4 is comprised of 2D (4,4) networks, and the adjacent sheets are extended into a 3D interdigitated framework via hydrogen-bonding interactions. Compounds 5 and 6 are based upon 3D pillared-layer frameworks constructed from [Cd(glu)]n/[Cd(adp)]n layers and the bib pillars. Both 7 and 8 are 3D frameworks with the same dia topology except that the former shows an abnormal 4-fold [2 + 2] interpenetrating mode and the latter is a single dia network without interpenetration. A comparison of compounds 1–8 demonstrates that the structure diversities may be greatly induced by increasing the spacer lengths and coordination modes of aliphatic dicarboxylic acids. Moreover, the photoluminescent properties of 1–8 are also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...