Epitaxial silicides: the case of Fe, Ni, and Ti†
Abstract
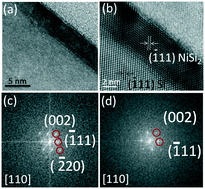
Ultra-thin epitaxial silicides were formed and their structures were examined by electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The epitaxial relationship between the silicides and Si was discovered and examined by electron diffraction patterns. The thickness of the silicide can be controlled by a double-sputtering process, rather than by the amount of deposited metals. Intermediate and low temperature phase silicides (C40-TiSi2 and Fe2Si) were observed, suggesting that process control is also an important factor, rather than the symmetry between the crystal structures of Si and silicide. This study is constructive to the basic understanding of the initial stage of the reaction that leads to epitaxial films on Si, as well as the epitaxial relationship of the crystalline layers. The observations may be useful for future design and application of nano-MOSFET and optoelectronics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...