Formation of reworkable nanocomposite adhesives by dielectric heating of epoxy resin embedded Fe3O4 hollow spheres†
Abstract
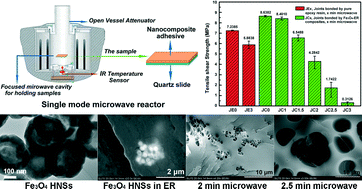
Epoxy resin (ER) thermosetting adhesives provide highly cross-linked 3-dimensional structures leading to highly stable and strong mechanical/physical performance in a wide range of bonding applications. However, such excellent physical attributes pose a significant challenge with respect to disassembly of the bonded adherends and previous disassembly methods have resulted in damage to the adherends. Hence, this paper presents a specifically engineered re-workable nanocomposite adhesive, created by embedding dielectric sensitive Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres (HNSs) in epoxy resin. This nanocomposite adhesive can be completely degraded by dielectric heating, resulting in facile disassembly of bonded adherends. FESEM and 3D Micro-CT characterisation demonstrates good dispersibility of the HNSs in cured ER, while the dielectric degradation performance and hardness/modulus were investigated by FESEM and nanoindentation. Results show that the Fe3O4 HNSs can effectively convert the microwave energy into thermal energy to significantly degrade the mechanical properties of the adhesive modulus and hardness by 83.4% and 90%, respectively. FESEM and HRTEM imaging attributes the reduction in nanocomposite adhesive properties to the formation of spatial voids nucleating from the embedded nanomaterials. Prior to dielectric heating, tensile loaded single lap-shear bonded joint tests indicated that the nanocomposite adhesive was 19.3% stronger than its neat ER adhesive counterpart due a nano-reinforcement toughening mechanism. However, after 3 minutes of dielectric heating exposure, the nanocomposite adhesive joint strength was reduced by 96.3% compared to just 18.7% for the neat ER adhesive, demonstrating the excellent re-workable performance of our new nanocomposite adhesive.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Crystal engineering of composite materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...