Rational design and synthesis of an amino-functionalized hydrogen-bonded network with an ACO zeolite-like topology for gas storage†
Abstract
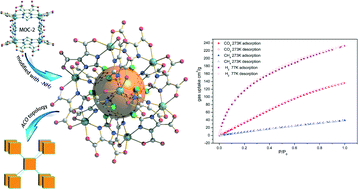
Based upon the typically hydrogen-bonded network, metal–organic cubes, the amino functional group was first introduced onto the surface of the cube to raise the polarizability of the framework by in situ hydrolysis of the precursor 2-amino-4,5-dicyanoimidazole (ADCIm) with octahedral In3+ ions under solvothermal conditions, resulting in a supramolecular network with very high CO2 (135.8 cm3 g−1 at 273 K/1 atm) and H2 (2.03 wt% at 77 K/1 atm) adsorption capacities and an exceptional thermostability range up to 416 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...