Two-sided effects of strong hydrogen bonding on the stability of dihydroxylammonium 5,5′-bistetrazole-1,1′-diolate (TKX-50)
Abstract
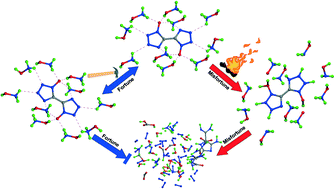
Dihydroxylammonium 5,5′-bistetrazole-1,1′-diolate (TKX-50) is a recently synthesized energetic ionic salt (EISs) with some excellent properties including high energy content, high density, low impact sensitivity and low toxicity, and therefore is a promising alternative energetic material. In contrast to commonly applied energetic CHON materials, TKX-50 features strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds (HBs). However, the effects of these strong HBs on its important properties remain unclear. We report herein the two-sided effects of the strong HBs on the stability of TKX-50, through ab initio simulations on shear deformation and thermal decomposition. That is, on the one hand, the strong HBs in TKX-50 lead to a layer-like arrangement of the cations and dianions in the (010) planes with the adjacent layers connected only by two types of weakest HBs, which facilitates the conversion of external kinetic energy into interlayer sliding, and contributes to low impact sensitivity; on the other hand, the extensive HBs in TKX-50 act as a potential source to facilitate H-transfer (including proton transfer), which accelerates subsequent thermal decomposition, and thus deteriorates the thermal stability of TKX-50 relative to its notably low impact sensitivity. These two-sided effects of the strong HBs in a TKX-50 crystal should be useful to understand properties of other EISs, in which strong HBs are universal, and enrich the knowledge of the sensitivity mechanism of energetic materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...