Monitoring structural changes in intrinsically disordered proteins using QCM-D: application to the bacterial cell division protein ZipA†
Abstract
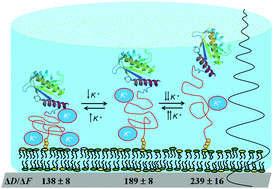
The sensitivity of QCM-D to molecular hydrodynamic properties is applied in this work to study conformational changes of the intrinsically disordered protein ZipA. Acoustic measurements can clearly follow ZipA's unstructured domain expansion and contraction with salt content and be correlated with changes in the hydrodynamic radius of 1.8 nm or less.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...