Acidic pH-induced charge-reversal nanoparticles for accelerated endosomal escape and enhanced microRNA modulation in cancer cells†
Abstract
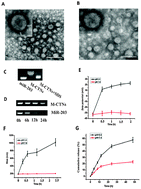
pH-Induced charge-reversal nanoparticles incorporating microRNA (miRNA) were engineered through a single-step self-assembly of polyelectrolyte complexes. We found that the endosomal/lysosomal acidic environment could trigger the charge reversal of the nanoparticles from negative charge to positive charge and induce the structure alteration of the nanoparticles, which in turn led to accelerated endosomal escape and enhanced miRNA modulation in esophageal cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...