Self-assembling oligothiophene–bolaamphiphiles for loading and controlled release of doxorubicin into living cells†
Abstract
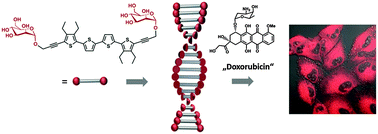
Design and synthesis of symmetric mannose-functionalized oligothiophenes is reported. Self-organization of these bolaamphiphiles in solution and in the solid state was investigated by optical and AFM experiments. Fluorescence measurements revealed efficient loading and pH-dependent release of the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin. Delivery and release of the active drug into viable A549 cells as well as chirality-dependent cellular toxicity of the bolaamphiphilic transporter were evident from in vitro experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...