Optimization and validation of an environmentally friendly method for zinc determination in new and used lubricating oil samples
Abstract
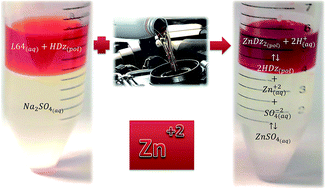
This work presents the optimization and validation of a new environmentally friendly method for zinc quantification in new and used lubricating oil samples, using, for the first time, the extracting agent diphenylthiocarbazone (dithizone) associated with the aqueous two-phase system (ATPS). This element can be used as an additive in new samples or to indicate the wear of mechanical components in used samples. The procedure for extraction and quantification of Zn(II) in aqueous two-phase systems formed by triblock copolymers (L35 or L64), salt (sulphate, citrate or sodium tartrate), and water as a function of several experimental parameters was investigated. The optimized process led to maximum extraction of Zn(II) (107 ± 3)%, using the following conditions: tie-line length (TLL) of 33.55% (w/w); dithizone/zinc molar ratio of 10; pH of 12.0 and mass ratio of the phases equal to 0.5 in a system composed of copolymer L64 + Na2SO4 + H2O. This method was validated using new lubricating oil sample that has a linear ion concentration range from 0.0 to 1.4 μg g−1. This technique showed low limits of detection (0.03 μg g−1) and quantification (0.13 μg g−1). Moreover, the trueness was evaluated against trend and recovery, ranging from 89 to 98% and 88 to 110%, respectively. The coefficients of variation remained between 1.9% and 6.6% for three different concentrations within the linear range. After validation, the method was applied for quantification of Zn(II) in eight new and four used samples of lubricating oil, and one reference material for interlaboratory testing. The results obtained by the ATPS method did not differ significantly from the results obtained by the standard method ASTM D5185 at 95% confidence level, according to the t-Student test. The proposed method is a simple, fast, efficient and safe alternative for zinc monitoring in lubricating oil samples compared to the methods used in the petrochemical industry. Moreover, it eliminates the need to use toxic organic solvents and enables reducing the sample mass and using inorganic standards.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...