Development of a low level detection method for 2-chloromalonaldehyde in active pharmaceutical ingredients by HILIC separation
Abstract
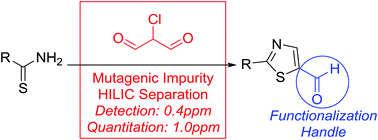
2-Chloromalonaldehyde (2-ClMA) is utilized in the pharmaceutical sector as a reagent to form thiazole heterocycles which can be further functionalized. This present work describes a hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) strategy for the trace analysis of 2-ClMA in pharmaceutical materials. Several method development aspects as well as a general mutagentic impurity control strategy for 2-ClMA are reviewed and discussed. The method as described has a reporting quantitation limit (QL) of 1 ppm and a reporting detection limit of 0.4 ppm for 2-ClMA with respect to a sample concentration of 10 mg mL−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...