Two-channel image analysis method for the screening of OBOC libraries†
Abstract
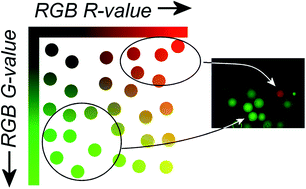
The split-synthesis approach offers a quick and easy method for producing a large diversity of substances for the discovery of novel protein ligands. Screening of the resulting one-bead-one-compound (OBOC) libraries with fluorescently labelled proteins is not trivial, however, since the resin beads can display significant autofluorescence. Here we present a simple two-channel microscopy image-based screening method for OBOC libraries on TentaGel MB-HMBA resin using tracers labelled with fluorophores. Bead images are taken at short exposure times in the RHO and FITC channels to keep photobleaching of the fluorophores at a minimum. Simple RGB colour vector addition ensures the identification of beads with high fluorescence intensities in the RHO channel. Pre-sorting of the library to exclude highly fluorescent beads is not necessary. The presented method is especially suited for small laboratories without automation equipment. By screening a library with a maximum of 117 649 peptoid hexamers we discovered 18 sequences that bind the human chemokine interleukin-8 (CXCL8) with affinities between 11 μM and 112 μM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...