A novel electrochemical sensor for 17β-estradiol from molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres and multi-walled carbon nanotubes grafted with gold nanoparticles
Abstract
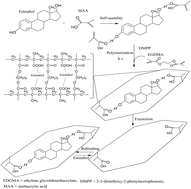
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) are generally a more stable material for sensing application. The high selectivity and sensitivity of MIPs for sensors can be achieved if the template molecule is imprinted in the polymer and this makes them an ideal alternative as a recognition element for sensors. A new electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres (MIPs) and multi-walled carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticle (MIP–MWCNT–AuNP) modified carbon screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) for the rapid detection of 17β-estradiol (E) hormone in serum samples has been successfully developed. Hydrophobic MIPs were synthesized using photopolymerization in emulsion form. The multi-walled carbon nanotube grafted with gold nanoparticles was firstly deposited onto a carbon screen-printed electrode for the purpose of accelerating electron transfer to the surface of the electrode. The MIP microspheres specific to the 17β-estradiol hormone, prepared via a facile photopolymerization technique, were coated onto the MWCNT–AuNP modified SPE. The presence of 17β-estradiol in biological samples could be detected with the sensor via absorption of 17β-estradiol into the deposited MIPs and this was monitored by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) at 0.6 V for the reduction of 17β-estradiol. Under optimal conditions, the sensor could detect the concentrations of 17β-estradiol from 1.0 × 10−15 to 1.0 × 10−6 M (R2 = 0.9921), with a detection limit of 2.5 × 10−16 M. The sensor based on MIP microspheres and the MWCNT–AuNP modified electrode demonstrated a stability of 55 days with good reproducibility (RSD < 5%, n = 5) and regenerability (RSD < 4%, n = 5). Using this sensor, the gender of the arowana fish determined via the level of 17β-estradiol using fish serum samples demonstrated good agreement with a conventional test kit based on the immuno-assay method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...