Gel electrophoretic and liquid chromatographic methods for the identification and authentication of cave and house edible bird's nests from common adulterants†
Abstract
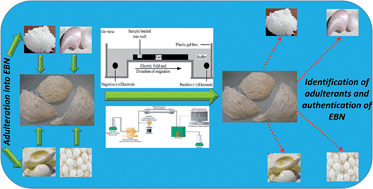
The increasing demands for edible bird's nests (EBNs) have remarkably increased their price. Presently, several fake materials are being adulterated into EBNs for the purpose of earning extra profits. In order to identify the adulterants and authenticate EBN, efforts were made to investigate and compare the protein and amino acid profiles of cave and house EBNs with white fungus, jelly, fish swimming bladder and egg white. The protein profiling indicated 10 bands for cave nests with two strong bands at 30 and 35 kDa. House nest proteins consisted of 9 bands with major bands at 120 and 140 kDa. White fungus displayed three dim bands at 22, 35 and 75 kDa whereas egg white was found to contain two predominant bands at 35 and 75 kDa. Fish swimming bladder showed substantial streaking of protein bands after dilution whereas the protein profile of jelly did not present any band. The amino acid analysis revealed that EBN consisted of 17 types of amino acids. The major amino acids in cave and house nests were aspartic acid, arginine, histidine & leucine, and aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine & leucine, respectively. White fungus consisted of 16 types of amino acids in concentrations lower than that in EBN samples. Fish swimming bladder was rich in 6 amino acids. Egg white contained 16 types of amino acids with aspartic acid, glutamic acid, leucine and lysine in major quantities. However, jelly was found to contain no amino acids at all. Both the analytical procedures provided finger print profiles of the protein and amino acid compositions of the cave and house nests distinct from the adulterants. These results taken together can be used for the identification and authentication of any of these fake materials in EBN.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...