Selective recognition and imaging of bacterial model membranes over mammalian ones by using cationic conjugated polyelectrolytes†
Abstract
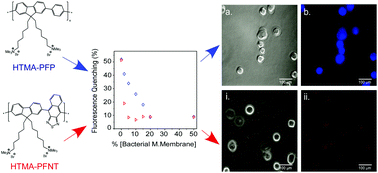
The development of new tools for the detection and fluorescence imaging of bacteria is of great interest in clinical diagnosis and food and environmental safety. In this work, we have explored the ability of two cationic fluorene-based conjugated polyelectrolytes, HTMA-PFP and HTMA-PFNT, emitting in the blue and red spectral regions respectively, to selectively label bacterial over mammalian cells. With this end in view, vesicles with lipid compositions mimicking those of bacterial or mammalian membranes were used as model membranes to explore the interaction of the polyelectrolytes with both systems in samples containing either a single type of vesicle or a mixture of both. Changes in the intrinsic fluorescence of HTMA-PFP and HTMA-PFNT were used to quantify the affinity of these polyelectrolytes for the model lipid membranes, while quenching experiments were employed to evaluate their selectivity to each lipid system. In addition, fluorescence microscopy experiments were performed to check the ability of polyelectrolytes to label the vesicles without affecting their integrity. Results showed that both polyelectrolytes rapidly label the model vesicles but they preferentially bind to those mimicking bacterial membranes, HTMA-PFNT being much more selective to this type of membranes than HTMA-PFP. Preliminary experiments with living bacteria and mammalian cells support this conclusion, showing that in samples with both types of cells together, HTMA-PFNT only images the bacterial cells, thus evidencing its potential use for the selective recognition and imaging of bacterial presence.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...