Design of luciferase-displaying protein nanoparticles for use as highly sensitive immunoassay detection probes
Abstract
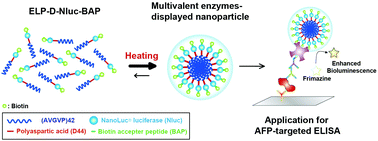
In this study, we developed a protein nanoparticle-based immunoassay to detect cancer biomarkers using a bioluminescent fusion protein. This method relies on the use of protein nanoparticles comprised of genetically-engineered elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) fused with poly-aspartic acid tails (ELP-D), previously developed in our lab. The sizes of the self-assembled ELP-D nanoparticles can be regulated at the nanoscale by charged repulsion of the poly-aspartic acid chains. To improve the sensitivity of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), we herein demonstrate the multivalent display of NanoLuc® (Nluc) luciferase and a biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) on the surfaces of ELP-D nanoparticles, and demonstrate the sensitivity of these multivalent nanoparticles as detection probes. The fusion protein comprised of ELP-D and Nluc-BAP (ELP-D-Nluc-BAP) was found to form nanoparticles with Nluc and BAP displayed multivalently on their surfaces. Moreover, the use of the nanoparticles in ELISA resulted in a detection sensitivity for α-fetoprotein (AFP) about 10 times higher than that of an assay relying on the use of the monomeric version of the fusion protein. Taken together, ELP-D-based nanoparticles displaying multivalent luciferases on their surfaces enable the construction of an ELISA with enhanced sensitivity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent Open Access Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...