Sensitive electrochemical detection of nitric oxide based on AuPt and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites†
Abstract
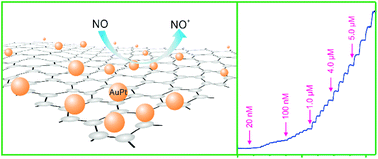
Since nitric oxide (NO) plays a critical role in many biological processes, its precise detection is essential toward an understanding of its specific functions. Here we report on a facile and environmentally compatible strategy for the construction of an electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and AuPt bimetallic nanoparticles. The prepared nanocomposites were further employed for the electroanalysis of NO using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and amperometric methods. The dependence of AuPt molar ratios on the electrochemical performance was investigated. Through the combination of the advantages of the high conductivity from rGO and highly electrocatalytic activity from AuPt bimetallic nanoparticles, the AuPt–rGO based NO sensor exhibited a high sensitivity of 7.35 μA μM−1 and a low detection limit of 2.88 nM. Additionally, negligible interference from common ions or organic molecules was observed, and the AuPt–rGO modified electrode demonstrated excellent stability. Moreover, this optimized electrochemical sensor was practicable for efficiently monitoring the NO released from rat cardiac cells, which were stimulated by L-arginine (L-arg), showing that stressed cells generated over 10 times more NO than normal cells. The novel sensor developed in this study may have significant medical diagnostic applications for the prevention and monitoring of disease.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...