A single-label fluorescent derivatization method for quantitative determination of neurotoxin in vivo by capillary electrophoresis coupled with laser-induced fluorescence detection†
Abstract
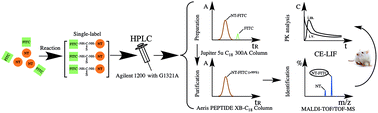
Neurotoxin (NT), a short-chain α-neurotoxin, is the main neurotoxic protein identified from the venom of Naja naja atra. As an effective drug for the analgesis of advanced cancer patients, NT lasts longer than morphine and does not cause addiction. However, achieving a sensitive and high-resolution measurement of NT is difficult because of the extra-low content of NT in vivo. Therefore, developing a novel method to quantify NT is essential to study its pharmacokinetics in vivo. Although NT contains four primary amine groups that could react with the thiourea in fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), we developed a simple and reproducible single-label fluorescent derivatization method for NT which is related to the reaction of N-terminal α-amino of NT alone under optimized derivatization conditions. Furthermore, neurotoxin labelled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (NT-FITC) was prepared by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with a purity value higher than 99.29% and identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS. Finally, NT-FITC could be detected at 0.8 nmol L−1 in rat plasma using capillary electrophoresis coupled with laser induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF). In this paper, the established method robustly and reliably quantified NT labelled with FITC via intravenous and intramuscular administrations in vivo. In addition, this work fully demonstrated the pharmacokinetic characteristics of NT in vivo, which could reduce the risk of drug accumulation, optimize therapies, and provide sufficient evidence for the rational use of NT in clinical and research laboratories.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...