Real-time quantitative nicking endonuclease-mediated isothermal amplification with small molecular beacons†
Abstract
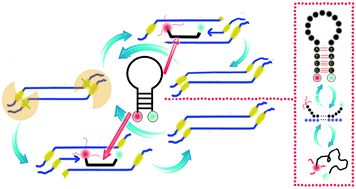
Techniques of isothermal amplification have recently made great strides, and have generated significant interest in the field of point-of-care detection. Nicking endonuclease-mediated isothermal amplification (NEMA) is an example of simple isothermal technology. In this paper, a real-time quantitative nicking endonuclease-mediated isothermal amplification with small molecular beacons (SMB-NEMA) of improved specificity and sensitivity is described. First, we optimized the prohibition of de novo synthesis by choosing Nt·BstNBI endonuclease. Second, the whole genome was successfully amplified with Nt·BstNBI (6 U), betaine (1 M) and trehalose (60 mM) for the first time. Third, we achieved 10 pg sensitivity for the first time after adding a small molecular beacon that spontaneously undergoes a conformational change when hybridizing to target, and the practical test validated the assay's application. The small molecular beacon has a similar melting temperature to the reaction temperature, but is approximately 10 bp shorter than the length of a traditional molecular beacon. A new threshold regulation was also established for isothermal conditions. Finally, we established a thermodynamic model for designing small molecular beacons. This multistate model is more correct than the traditional algorithm. This theoretical and practical basis will help us to monitor SMB-NEMA in a quantitative way. In summary, our SMB-NEMA method allows the simple, specific and sensitive assessment of isothermal DNA quantification.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...