Cellulose/boron nitride core–shell microbeads providing high thermal conductivity for thermally conductive composite sheets†
Abstract
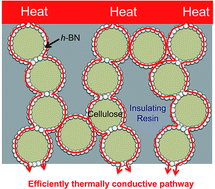
We fabricated sheets with high thermal conductivity in a way that required less filler. Our approach is as follows: (1) we used core–shell spherical microbeads as the thermally conductive filler; (2) we developed cellulose/h-boron nitride (BN) core–shell spherical microbeads using phase separation of a cellulose xanthate aqueous solution (viscose); (3) we hybridized the cellulose/h-BN core–shell microbeads with epoxy resin using compression molding. This process reduced the amount of h-BN required because the microbeads efficiently formed thermally conductive pathways among the shells in the insulating resin. The thermal conductivities of the resulting sheet in the thickness and in-plane directions were 10.6 and 15.6 W m−1 K−1, respectively, using only 48.5 vol% h-BN. In contrast, the thermal conductivities of the composite sheet with 75 vol% of naked h-BN particles were 6.31 and 22.9 W m−1 K−1 in the thickness and in-plane directions, respectively. This large difference resulted from the anisotropic structure of h-BN. The changes in thermal conductivity with h-BN content were inconsistent with percolation theory, when using the cellulose/h-BN core–shell microbeads as a filler. The thermally conductive sheets fabricated with microbeads exhibited thermal conductivities several times greater than that of sheets fabricated with naked h-BN. This indicated that thermally conductive pathways had formed in the insulating resin.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2D Materials: Explorations Beyond Graphene

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...