Red raspberry decreases heart biomarkers of cardiac remodeling associated with oxidative and inflammatory stress in obese diabetic db/db mice†
Abstract
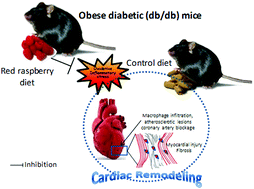
Early diagnosis of risks of heart disease can be critical to fight cardiovascular diseases (CVD) associated with obesity and diabetes and for the implementation of nutritional interventions. The objective of this study was to investigate the cardioprotective effects of red raspberry consumption in the obese diabetic (db/db) mice using proteomic analysis as a tool. Hearts harvested from db/db mice fed an isocaloric diet (AIN-93G, control group) or AIN-93G supplemented with freeze-dried raspberry (raspberry group) for eight weeks were analyzed for changes in protein expression. Bioinformatics and pathway analysis of proteomic data detected in >50% samples were scrutinized with Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). Histologic analysis, adipokines and lipid quantification in heart tissues were assessed as end points for disease biomarkers. Results from proteomic data identified five proteins unique to the control group involved in cardiac remodeling and one involved in stress response. Twenty-five proteins expressed in both groups were differentially downregulated in the raspberry group (p < 0.05) within 0.25–0.7-fold of control. Out of these, seven were involved in cardiac remodeling (e.g. natriuretic peptide precursor type A, 0.25-fold of control), and five were involved in stress response (e.g. glutathione S-transferase A4, 0.49-fold of control). However, no significant differences between raspberry and control groups were detected in heart lipid composition, adipokines, and morphology within the study timeframe. In conclusion, raspberry consumption may be effective in decreasing the levels of oxidative and inflammatory stress that promote morphological changes in the heart at an older age, thus preventing or delaying heart diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...