Alkyl chain modulated cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity of bioinspired amphiphilic selenolanes†
Abstract
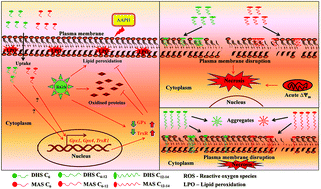
A series of amphiphilic conjugates of dihydroxy selenolane (DHS) and monoamine selenolane (MAS), which we had previously reported to inhibit lipid peroxidation and assist the oxidative protein folding reaction respectively in cell free systems, were evaluated for cytotoxicity, associated mechanisms and antioxidant effects in cells. Our results indicated that a fatty acid/alkyl group of variable chain lengths (C6–14) as a lipophilic moiety of the DHS/MAS conjugates not only improved their ability to incorporate within the plasma membrane of cells but also modulated their cytotoxicity. In the concentration range of 1–50 μM, C6 conjugates were non-toxic whereas the long chain (≥C8) conjugates showed significant cytotoxicity. The induction of toxicity investigated by the changes in membrane leakage, fluidity, mitochondrial membrane potential and annexin-V–propidium iodide (PI) staining by using flow cytometry revealed plasma membrane disintegration and subsequent induction of necrosis as the major mechanism. Further, the conjugates of DHS and MAS also showed differential as well as nonlinear tendency in cytotoxicity with respect to chain lengths and this effect was attributed to their self-aggregation properties. Compared with the parent compounds, C6 conjugates not only exhibited better antioxidant activity in terms of the induction of selenoproteins such as glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1), GPx4 and thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) but also protected cells from the AAPH induced oxidative stress. In conclusion, the present study suggests the importance of hydrophilic–lipophilic balance (HLB) in fine tuning the toxicity and activity of bioinspired amphiphilic antioxidants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...