CTAB induced mitochondrial apoptosis by activating the AMPK–p53 pathway in hepatocarcinoma cells†
Abstract
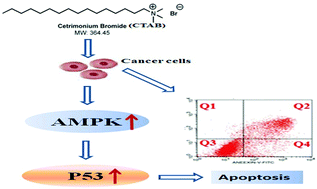
The reprogramming of energy metabolism as a new concept is emerging and is one of the hallmarks of cancer. CTAB, known as a quaternary ammonium compound with the activity of inhibiting mitochondrial H-ATP synthase, has shown the potential to influence cell energy metabolism. In this study, we investigated the effects and the underlying mechanisms of CTAB on liver cancer cells. The results showed that CTAB reduced the cell viability of various hepatocarcinoma cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The results showed that CTAB induced mitochondrial apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells by activating AMPK and p53 signaling pathways. Our study sheds light on CTAB as a promising cancer therapeutic candidate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...