Effect of Nb and Ta substitution on donor electron transport and ultrafast carrier dynamics in anatase TiO2 thin films†
Abstract
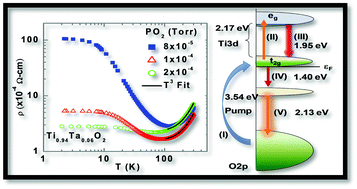
Ta and Nb substituted TiO2 are important transparent conducting oxides that have potential for applications in photovoltaics, photocatalysis, and water splitting/CO2 sequestration. In addition to donating electrons, what are the effects of Nb and Ta substitution? Here we observe strong experimental evidence that Ta and Nb substitution induces large and small polarons in anatase TiO2 epitaxial thin films. The degenerate donor electrons (from both Nb and Ta) show a high temperature T3 dependence on electrical resistivity, which confirms the presence of large polarons, along with room temperature metallic transport. This is further confirmed by the enhancement in the electron effective mass, which was estimated from thermopower measurements. Femtosecond transient absorption (fs-TA) reveals the life time of the Ti-t2g and eg levels and the separation of these levels are consistent with the X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) measurement. In addition, fs-TA reveals the presence of small polarons with a life time substantially >1 ns, which arises from defect levels and is a consequence of Ta and Nb substitution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) provides evidence of Ti3+, which may be identified as the defects responsible for the small polarons. These long-lived small polarons may provide a way to minimize recombination dynamics in TiO2-based electrodes for photo-excited devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...