Critical roles of Mn-ions in enhancing the insulation, piezoelectricity and multiferroicity of BiFeO3-based lead-free high temperature ceramics
Abstract
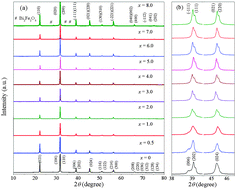
A lead-free multiferroic ceramic of BiFe0.96Sc0.04O3–BaTiO3 is a type of ABO3 perovskite structure, belonging to the R3c space group, but exhibiting poor insulation and weak multiferroicity. In this work, the critical roles of Mn-ions in tailoring the electrical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3-based materials are revealed: the introduction of MnO2 into BiFe0.96Sc0.04O3–BaTiO3 induces a dramatic improvement in insulation, piezoelectricity and multiferroicity. New compositions of BiFe0.96Sc0.04O3–BaTiO3 + x mol% MnO2 were synthesized by a conventional solid-state reaction method. All the ceramics possess a perovskite structure, and a morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) of rhombohedral and monoclinic phases is formed at x = 0.5–1.0. The formation of 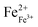 and
and 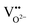 is noticeably suppressed and the resistivity of the ceramics is increased by ∼100 times after the addition of 0.5–1.0 mol% MnO2, which make the ceramic polarizable and thus give strong ferroelectricity and considerable piezoelectricity. The ceramics with the MPB composition exhibit high electrical insulation (R = 1.2–1.7 × 1010 Ω cm), good piezoelectricity (d33 = 123–143 pC N−1, kp = 0.34–0.35), strong ferroelectricity (Pr = 13.1–17.6 μC cm−2), high Curie temperature (590–596 °C) and excellent temperature stability of piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties. These improvements are greatly associated with the contribution of Mn ions in the ceramics. Surprisingly, sharply enhanced ferromagnetism with Mr = 0.4946 emu g−1 and Ms = 1.0298 emu g−1 is obtained in the ceramic with x = 7.0, almost one thousand times larger than that of an un-doped ceramic. The origin of unusual ferromagnetism is associated with significant changes in magnetic ordering caused by Mn doping. The high magnetoelectric effect (α33 = 429.6 mV cm−1 Oe−1) is obtained after the addition of 2.0 mol% Mn ions. Our study suggests that the present ceramics may have potential applications in advanced memory devices as promising lead-free high temperature piezoelectric and multiferroic materials.
is noticeably suppressed and the resistivity of the ceramics is increased by ∼100 times after the addition of 0.5–1.0 mol% MnO2, which make the ceramic polarizable and thus give strong ferroelectricity and considerable piezoelectricity. The ceramics with the MPB composition exhibit high electrical insulation (R = 1.2–1.7 × 1010 Ω cm), good piezoelectricity (d33 = 123–143 pC N−1, kp = 0.34–0.35), strong ferroelectricity (Pr = 13.1–17.6 μC cm−2), high Curie temperature (590–596 °C) and excellent temperature stability of piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties. These improvements are greatly associated with the contribution of Mn ions in the ceramics. Surprisingly, sharply enhanced ferromagnetism with Mr = 0.4946 emu g−1 and Ms = 1.0298 emu g−1 is obtained in the ceramic with x = 7.0, almost one thousand times larger than that of an un-doped ceramic. The origin of unusual ferromagnetism is associated with significant changes in magnetic ordering caused by Mn doping. The high magnetoelectric effect (α33 = 429.6 mV cm−1 Oe−1) is obtained after the addition of 2.0 mol% Mn ions. Our study suggests that the present ceramics may have potential applications in advanced memory devices as promising lead-free high temperature piezoelectric and multiferroic materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...