Tensile properties and in vitro degradation of P(TMC-co-LLA) elastomers†
Abstract
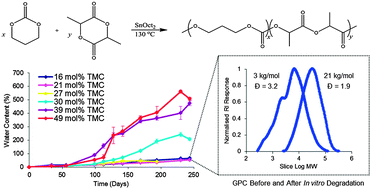
P(TMC-co-LLA) elastomers have shown great potential for various biomaterials applications. This study investigated properties key to such applications. Six statistical copolymers with 16 to 49 mol% TMC were synthesized and it was found that the LLA sequence length changed from 14 to 3 for the copolymer series while the ![[M with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_004d_0304.gif) n decreased from 63 to 31 kg mol−1 with increasing TMC content. The thermal properties showed lower Tg values with increasing TMC content which agreed with the Fox equation. Solvent cast films exhibited Young's modulus values between 2.8 and 271 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 0.6–15.5 MPa and elongation at failure from 356 to 1287%. In vitro degradation in PBS at 37 °C over 34 weeks demonstrated an induction period of 9 weeks during which the water content was minimal for all copolymers. Copolymer films with 21 or greater mol% TMC were found to undergo homogeneous bulk degradation, while films with 16 mol% TMC underwent heterogeneous bulk degradation.
n decreased from 63 to 31 kg mol−1 with increasing TMC content. The thermal properties showed lower Tg values with increasing TMC content which agreed with the Fox equation. Solvent cast films exhibited Young's modulus values between 2.8 and 271 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 0.6–15.5 MPa and elongation at failure from 356 to 1287%. In vitro degradation in PBS at 37 °C over 34 weeks demonstrated an induction period of 9 weeks during which the water content was minimal for all copolymers. Copolymer films with 21 or greater mol% TMC were found to undergo homogeneous bulk degradation, while films with 16 mol% TMC underwent heterogeneous bulk degradation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...