A delocalizable cationic headgroup together with an oligo-oxyethylene spacer in gemini cationic lipids improves their biological activity as vectors of plasmid DNA†
Abstract
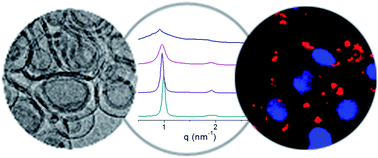
Lipoplex nano-aggregates constituted of plasmid DNA (pDNA) pEGFP-C3 and mixed cationic liposomes, consisting of several percentages of a gemini cationic lipid (GCL) of the 1,2-bis(hexadecyl imidazolium) oxyethylene series, referred to as (C16Im)2(C2O)n, with oxyethylene spacers (n = 1, 2 or 3) between the imidazolium cationic groups and the DOPE zwitterionic helper lipid, have been characterized by various biophysical and biological approaches carried out at several GCL compositions (α), and either the mass or the effective charge ratio of the lipoplex. The electrochemical study by ζ-potential confirms that the three GCLs yield a 10% lower effective charge than the nominal one, while compacted pDNA yields only a 25% effective negative charge. The SAXS study reveals, irrespective of the spacer length (n) and effective charge ratio (ρeff), the presence of two lamellar structures, i.e., one (Lα,main) in the whole GCL composition and another (Lα,DOPE,rich) with higher periodicity values that coexists with the previous one at low GCL composition (α = 0.2). The cryo-TEM analysis shows two types of multilamellar structures consisting of cationic lipidic bilayers with pDNA sandwiched between them: a cluster-type (C-type) at low α = 0.2 and a fingerprint-type (FP-type) at α ≥ 0.5, both with similar interlamellar spacing (d) in agreement with the Lα,main structure determined by SAXS. Transfection efficacies (TEs) of each lipid mixture were determined in four different cell lines (HEK293T, HeLa, Caco-2 and A549) at several α and ρeff values in the absence and presence of serum (FBS). The optimized formulations (α = 0.2 and ρeff = 2.0) substantially transfect cells much better than a commercial transfection reagent, Lipofectamine 2000 and previously studied efficient lipoplexes containing other cationic head groups or spacers both in the absence and presence of serum. The activity of optimized formulations may be attributed to the combination of several factors, such as: (a) the fusogenic character of DOPE which results in higher fluidity of the lipoplexes at α = 0.2, (b) the coexistence of two lamellar structures at α = 0.2 that synergizes the TE of these lipid vectors, and mainly (c) the higher biocompatibility of the GCLs reported in this work due to the presence of two imidazolium cationic groups together with an oligo-oxyethylene spacer. The length of the spacer in the GCL seems to have less impact, although (C16Im)2(C2O)n/DOPE-pDNA lipoplexes with n = 1 and 3 show higher gene transfection than n = 2. All the optimum formulations reported herein are all highly efficient with negligible levels of toxicity, and thus, may be considered as very promising gene vectors for in vivo applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...