Cellulose nanofiber–titania nanocomposites as potential drug delivery systems for dermal applications†
Abstract
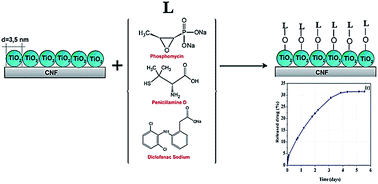
In this work, new efficient drug delivery systems based on cellulose nanofiber–titania nanocomposites grafted with three different types of model drugs such as diclofenac sodium, penicillamine-D and phosphomycin were successfully synthesized and displayed distinctly different controlled long-term release profiles. Three different methods of medicine introduction were used to show that various interactions between TiO2 and drug molecules could be used to control the kinetics of long-term drug release. All synthesis reactions were carried out in aqueous media. The morphology, chemical structure and properties of the obtained materials were characterized by SEM, TEM and AFM microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, X-ray diffraction, and TGA analysis. According to FT-IR and UV-Vis spectroscopy data, the titania binds to cellulose nanofibers via formation of ester bonds and to drug molecules via formation of surface complexes. The drug release kinetics was studied in vitro for diclofenac sodium and penicillamine-D spectrophotometrically and for phosphomycin using a radio-labeling analysis with 33P-marked ATP as a model phosphate-anchored biomolecule. The results demonstrated that the obtained nanocomposites could potentially be applied in transdermal drug delivery for anesthetics, analgesics and antibiotics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...