Gold nanoparticles as drug carriers: a contribution to the quest for basic principles for monolayer design†
Abstract
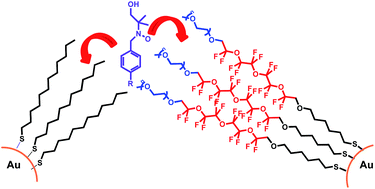
Two structurally different water-soluble homoligand gold nanoparticle systems, one featuring a rigid fluorous monolayer in the proximity of the gold core and the other featuring a flexible fluorinated region in a distal position, were studied as putative hosting systems by determining their binding constants for a series of fluorinated and non-fluorinated radical probes by means of ESR spectroscopy. Comparison of the binding constants obtained with hydrogenated homoligand nanoparticles of similar structure used as the reference evidenced that the binding of both hydrogenated and fluorinated guests is favoured in the presence of fluorinated nanoparticles. In addition, a flexible fluorinated monolayer acts as a better hosting system than the more rigid counterpart. In the latter case decreasing the size of the nanoparticles causes a small decrease of the binding affinities for both hydrogenated and fluorinated guests. The same nanoparticle systems were analysed for their ability to retard the phase transfer of a fluorescent dye from an aqueous solution to a toluene layer. All of the nanoparticles studied produced a significant decrease of the phase transfer rate of the dye because of the efficient interaction with the monolayer. These data support the introduction of fluorinated moieties in the monolayer of gold nanoparticles as a novel design tool for the development of drug delivery systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...