Cysteine-containing oligopeptide β-sheets as redispersants for agglomerated metal nanoparticles
Abstract
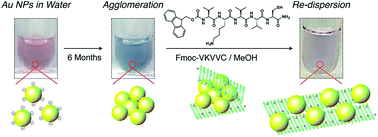
Oligopeptide β-sheets comprising a fluorenyl methoxy carbonyl (Fmoc) group on its N-terminus and five amino acid residues of cysteine, lysine and valine displays redispersive properties with respect to agglomerated metal nanoparticles (MNPs, M = Au, Cu, Pt and Pd). The ligand-free MNPs prepared by a laser ablation technique in liquid maintain a high dispersion state due to the inherent surface charges delivered by anionic species present in solution, but may agglomerate after the preparation depending on concentration or salinity. We show how the agglomerated MNPs can be returned to the dispersed state by adding the Fmoc-oligopeptide β-sheets in methanol, as characterized by photoabsorption spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Systematic studies in which we vary the concentration, the amino acid sequences and the secondary structures of a series of the oligopeptides clarify that the β-sheet structure is essential for the redispersion of the MNPs, where metal-binding thiol groups are integrated on one side and positively charged amino groups are located on the other side of the β-sheet. A possible mechanism for the redispersion may be that the agglomerated MNPs are subsequently enwrapped by the flexible β-sheets and gradually separated due to the reconstruction of peptide β-sheets under the assembly/disassembly equilibrium.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Artificial Photosynthesis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...